🦠 What Is Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is a serious bacterial infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium. It’s primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks (also called deer ticks). The disease is most common in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, and can lead to long-term health complications if not treated early.
📍 How Do You Get Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is not contagious between people. The main cause of transmission is:
-
A tick bite from an infected black-legged tick.
-
Ticks must be attached to the skin for at least 36–48 hours to transmit the bacteria.
Risk increases if you live in or travel to wooded or grassy areas — especially during late spring to early fall.
🚨 Common Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Symptoms vary by stage of the infection. Early detection is key.
🔹 Early Stage (3–30 days after tick bite):
-
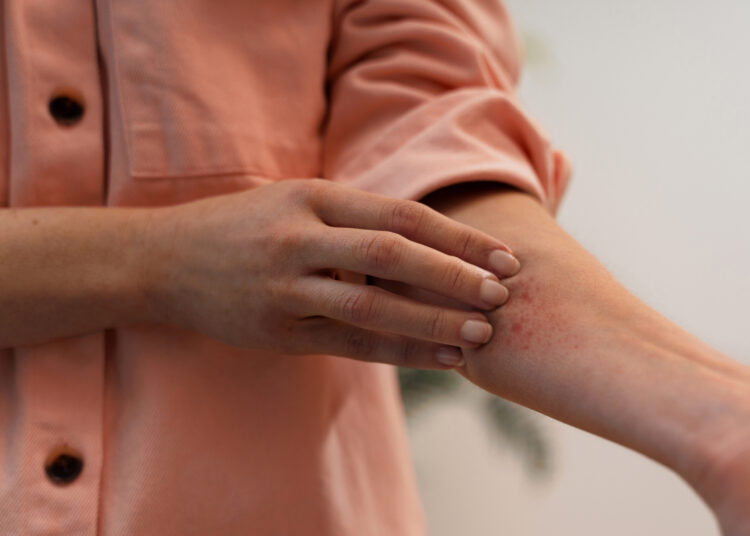
Erythema migrans (EM) rash – a red circular rash that may look like a bullseye
-
Fever or chills
-
Headache
-
Muscle and joint aches
-
Fatigue
-
Swollen lymph nodes
🔸 Later Stage (weeks to months later):
-
Severe joint pain and swelling (especially knees)
-
Neurological problems (e.g., meningitis, Bell’s palsy)
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Brain fog or memory issues
-
Numbness or tingling in hands or feet
🧪 How Is Lyme Disease Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose Lyme disease through a combination of:
-
Physical examination (presence of rash and symptoms)
-
Medical history, including potential tick exposure
-
Laboratory tests:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
-
Western blot test (used to confirm ELISA results)
-
Tests may not be accurate in the first few weeks, so doctors often rely on clinical judgment.
💊 Lyme Disease Treatment Options
When diagnosed early, Lyme disease is typically curable with antibiotics.
✅ First-line treatments:
-
Doxycycline (10–21 days)
-
Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime (for children or those allergic to doxycycline)
⚠️ Chronic or Late Lyme:
Some patients develop Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS), with symptoms lingering for months. Treatments may include:
-
Symptom management (e.g., pain relievers, physical therapy)
-
Cognitive therapy for brain fog
There is no proven benefit of long-term antibiotic use for PTLDS.
🛡️ How to Prevent Lyme Disease
Prevention is crucial, especially if you live in high-risk areas.
-
Wear long sleeves and pants when in tall grass or wooded areas
-
Use EPA-registered insect repellent
-
Shower within 2 hours of outdoor activity
-
Check your body for ticks after coming inside
-
Remove ticks promptly with fine-tipped tweezers
🌍 Global Relevance and Awareness
Lyme disease cases are rising globally, especially in temperate countries with dense vegetation. Countries like the United States, Germany, Sweden, and Canada report thousands of cases annually. Climate change and increasing tick populations have contributed to its spread.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Lyme disease is preventable, treatable, and manageable — especially when caught early. Being aware of the symptoms and knowing what to do after a tick bite can protect you and your family. Always consult a doctor if you suspect exposure or experience any unusual symptoms.